All About 5G: The Next Big Thing After WiFi
Who developed 5G?
There isn’t just one person or organisation responsible for the creation of 5G. It involves cooperation between many global regions. The creation of a unified standard is crucial for the effective advancement of 5G technology. The 3GPP established the standards for 5G technology in the middle of 2018. A group of seven regional organisations make up 3GPP.
Will 5G kill WiFi?
Currently, 5G technology is not designed to replace WiFi. In areas with questionable WiFi, 5G might offer an alternative. To attain the goal of robust connectivity, WiFi and 5G should collaborate and improve upon one another.
What underlying technologies make up 5G?
On OFDM, 5G technology is built. The term “OFDM” refers to the coding of digital data across several bandwidths and frequencies. 5G technology uses a 5G NR air interface in addition to OFDM.
How and when will 5G affect the global economy?
In critical industries, 5G technology could generate an additional $1.5 trillion by 2030, according to an analysis by Huawei.
According to STL, the benefits of 5G technology solutions might total $200 billion.
What does 5G mean for consumers?
For customers, a quicker mobile internet connection is just the start of what 5G technology can offer. With more devices being linked using this next-generation technology, the user will benefit from a stronger, more secure connection with faster speeds and lower latency. Consumers can anticipate self-driving cars, smart homes, virtual reality experiences for shopping, gaming, and watching athletic events, telemedicine, and remote health monitoring.
How do cities use 5G?
Sensors connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) will track and gather information on city traffic patterns, energy use, and air quality. This will make it easier for civic officials to manage their activities. Ambulances, fire trucks, and police cars will be able to reach their destination without interruption. Smart buildings would serve as hubs for the working population and be able to provide essential services without interruption. These are the advantages of 5G-enabled smart cities. Millions of gadgets will be interconnected to collect data and function according to supply and demand. Below are some of the industries that will be automated and networked for cities.
5G speed – How fast is 5G?
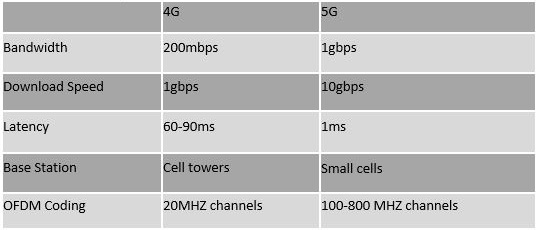
The reliability has been greatly enhanced, and the 5G speed is 20 times quicker than the previous generation. The theoretical maximum 5G download speed is 10gbps, compared to 4G technology’s 1gbps.
How does 5G work?
5G employs cell sites that utilise radio waves to transport data through sectors of the area. This idea has roots in earlier networks. Each cell site needs to be connected to a network, and 5G employs an OFDM network. This allows for more effective coding, which increases the speed of the 5G radio waves.
Does 5G change my home internet service?
A wireless solution is 5G. Cables are required for the Internet, which connects to modems, which connect to the home internet. It now appears that 5G and home internet will most likely coexist side by side. Due to its limiting parameters, 5G won’t be able to completely replace internet services shortly.
The wireless 5G reception could not be the same in urban and rural local geographies. The initial cost of 5G cellular services for consumers could be higher. Additionally, not all devices are 5G certified yet, so they might not function if the fifth generation is completely implemented.
What is 5G all about?
The next big thing in wireless technology networking is 5G. It is the fifth generation of wireless technology, to put it simply. Technology in its fifth generation is anticipated to be more advanced, faster, and larger. A much higher next-generation technology plane serves as the foundation for 5G architecture, which connects everything and everyone, including people, buildings, cities, sensors, smartphones, robots, and drones. It will be more advanced than current wireless technology in terms of data speeds, latency, system capacity, energy efficiency, and cost savings. For society and industry, it will bring new capabilities and opportunities. Here are a few examples of the lively 5G discussion:
“Connected automobiles will influence how people move about in the future, and next-generation mobile networks will raise the bar for in-car connectivity.” Alfons Pfaller, Audi AG’s Head of Infotainment Development
Ignacio Contreras, director of marketing at Qualcomm, predicted that the adoption of 5G will be even quicker than that of 4G, which was already moving along rather quickly.
According to Robert J. Topol, Intel’s general manager for 5G business and technology, “5G will be the post-smartphone era.” As far as connectivity goes, “phones are the first location to launch because [they] are such an anchor in our lives.”
In addition to artificial intelligence, Steve Koenig, senior director of market research for the Consumer Technology Association, noted that 5G is one of the signs of the impending data age.
What makes 5G different?
With current technology like 4G, we have mostly thought of connectedness as being between humans or between humans and the internet. But with 5G, that won’t be sufficient any longer.
The next logical step in connectivity is to link not just commonplace machines and gadgets to people, but also other machines. The idea behind 5G is to connect everything in our environment! A term like the Internet of Things (IoT), Virtual Reality (VR), and Artificial Intelligence will no longer be merely speculative connotations of what will happen in the future, with the number of connected devices globally anticipated to triple by 2030 to 25.4 billion. On the strength of 5G, all these incredible experiences will become available.
3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) claims that three key applications are improved by 5G to deliver value.
EMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) – greater network coverage, faster data rates, and improved streaming of ultra-HD video
Low latency, extremely dependable connection (URLLC) – faster and better communication in important areas like drones and robots
MMTC (Massive Machine-Type Communication) – Data generation, processing, and transmission between devices automatically with essentially no human involvement
To properly comprehend the phenomena of the fifth generation, let’s trace the development of several wireless technology generations:
First-generation mobile networks, or 1G, were developed in the 1970s and 1980s and only supported speech data. They were sent over radio waves unencrypted. Japan was a 1G revolution pioneer. Low coverage, poor sound quality, a lack of system compatibility, and unencrypted voice were all drawbacks of 1G.
In the 1990s, the phrase “2G” first surfaced. Digital and encrypted communications were being used. Data of greater calibre might be exchanged. It was possible to send text, photos, and multimedia communications. Telecommunications underwent a revolution as a result of this. Mobile cell towers started to appear, and businesses and consumers immediately embraced them. The smartphone was created.
Beginning in the early 2000s, 3G was developed. People could access data from anywhere in the world since online connectivity was standardised in this era. Two gigabits per second were outperformed by this by a factor of four. 3G improved call quality, video conferencing, streaming, and data transfer capabilities. The Blackberry launch contained features specific to this generation. Since the release of the iPhone in 2007, 3G technology has transformed smartphones from luxury goods to a necessity.
Apple, Google, and Facebook all played major roles in the development of 4G technology. Thanks to 4G technology, consumers now have access to high-quality video streaming. Today’s most popular technology, 4G technology, offers services for high-definition films, conferencing, and gaming. It only took a simple SIM card swap to go from 2G to 3G. For 4G, however, a shift in mobile devices is necessary.
5G: The fifth generation revolution is about to begin. Higher speed, lower latency, energy savings, and larger capacity systems are promised by this generation. With its better connectivity, 5G aims to provide network access to everyone, regardless of their location or social standing. 5G opens the door to technological advancements like telemedicine, self-driving cars, smart cities, smart factories, and virtual reality experiences for shopping, gaming, and sports viewing. It aims to broaden wireless internet services to the telecom and Internet of Things industries.
Consider 5G as a new, more advanced technology rather than the logical next step in the evolution of 4G.
Small cells will be used in 5G instead of cell towers, which were employed in earlier generations. Carriers will therefore spread out the deployment of high band 5G tiny cells. Additionally, 5G technology is designed to utilise 100 to 800 MHz channels rather than the 20 MHz of 4G as part of its OFDM coding. Keep in mind that the download speed increases with the channel level. As a result, 5G is 20 times quicker than the prior generation, has significantly lower latency, and has significantly increased reliability. A greater number of users can connect at once, and faster downloads are made possible by decreased latency.
Where is 5G being used | Industry Applications | Real Life Examples
Technology based on 5G is inclusive. The following are some of the sectors that 5G technology is transforming:
Smart structures and smart cities: Civic authorities will be able to efficiently manage operations with the use of IoT (Internet of Things) sensors that can monitor and collect data on air quality, energy usage, and traffic patterns for cities. Emergency vehicles will be able to connect to destinations without interruption, smart buildings will have essential utilities without interruption, and connected buildings will normalise remote working!
Manufacturing industry: AI will analyse massive amounts of data being gathered to automate human processes like quality control, standardisation, precision checking, and other similar tasks. Smart businesses will be able to use robots for risky/repetitive jobs thanks to end-to-end automation enabled by the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT).
Environment and agriculture: Data on weather, crop health, chemical levels, and insect prevalence will be transformed by connected devices to enable efficient labour allocation, cost and waste reduction, and increased yield. It will be possible to monitor the environment, including the flora and wildlife, and restore ecological balance in remote locations.
Telemedicine and healthcare: Remote diagnostics and procedures will become more prevalent, and medical device implants will easily capture and communicate patient health data to specialists, enabling the early detection of diseases.
Transportation and the auto industry: Real-time communication between self-driving cars and fixed roadway infrastructures will be available.
Virtual reality will become more practical, enabling remote working from distant areas or a genuine live sports stadium experience at home. Virtual reality will also be more useful for entertainment and live event experiences. The emergence of virtual shopping in several cities around the world would make downloading offline entertainment unnecessary.
How is STL Transforming the 5G scope?
STL was prepared for the revolution in 5G technology. Sterlite Technology Limited said in July 2020 that it would invest in 5G architecture to create an environment for Make in India. The investment would take the form of purchasing equipment, purchasing software, and hiring personnel. The goal that STL is pursuing is 5G India.
Anand Agarwal, Group CEO of STL, stated that the current telecom infrastructure is changing to a new digital network design that is virtual, convergent, disaggregated, and close to the edge. He continued by saying that STL is well-positioned to deliver next-generation digital networks for its customers internationally thanks to its 5G ecosystem and digital network integration skills.
About the future, STL is one of the leading Indian businesses engaged in 5G technology and has created a complete 5G ecosystem using its robust portfolio of wireless and optical technologies. With plans to invest 300 crores, STL has become one of the key 5G cable businesses in India. This will increase the optical fibre capacity between India and Europe from 18 to 33 million kilometres. In addition, STL has made a unique end-to-end investment in the development of completely programmable, open, and disaggregated Open RAN 5G-NR and Private LTE solutions that make use of edge convergence orchestration and real-time intelligence to improve network performance. For citizen networks, telcos, businesses, and governments, our portfolio of 5G-enabled wireless solutions comprise small cells, outdoor multi-band radio, and WiFi-6 solutions that adhere to Open RAN standards. Speed and connectivity in crowded locations could be considerably improved with these antennas and radio equipment. We also have RAN Intelligent Controller, Orchestration, and VNF solutions for telcos as part of our products!




